
Back بوابة:آسيا Arabic ܬܪܥܐ:ܐܣܝܐ ARC Portal:Asiya Azerbaijani Партал:Азія BE-X-OLD প্রবেশদ্বার:এশিয়া Bengali/Bangla دەروازە:ئاسیا CKB Portal:Asien German Portal:Asya DIQ Πύλη:Ασία Greek Portal:Asia Spanish

 Asia (/ˈeɪʒə/ AY-zhə, UK also /ˈeɪʃə/ AY-shə) is the largest continent in the world by both land area and population. It covers an area of more than 44 million square kilometers, about 30% of Earth's total land area and 8% of Earth's total surface area. The continent, which has long been home to the majority of the human population, was the site of many of the first civilizations. Its 4.7 billion people constitute roughly 60% of the world's population. Asia shares the landmass of Eurasia with Europe, and of Afro-Eurasia with both Europe and Africa. In general terms, it is bounded on the east by the Pacific Ocean, on the south by the Indian Ocean, and on the north by the Arctic Ocean. The border of Asia with Europe is a historical and cultural construct, as there is no clear physical and geographical separation between them. It is somewhat arbitrary and has moved since its first conception in classical antiquity. The division of Eurasia into two continents reflects East–West cultural, linguistic, and ethnic differences, some of which vary on a spectrum rather than with a sharp dividing line. A commonly accepted division places Asia to the east of the Suez Canal separating it from Africa; and to the east of the Turkish Straits, the Ural Mountains and Ural River, and to the south of the Caucasus Mountains and the Caspian and Black seas, separating it from Europe. China and India traded places as the largest economies in the world from 1 to 1800 CE. China was a major economic power for much of recorded history, with the highest GDP per capita until 1500. The Silk Road became the main east–west trading route in the Asian hinterlands while the Straits of Malacca stood as a major sea route. Asia has exhibited economic dynamism as well as robust population growth during the 20th century, but overall population growth has since fallen. Asia was the birthplace of most of the world's mainstream religions including Hinduism, Zoroastrianism, Judaism, Jainism, Buddhism, Confucianism, Taoism, Christianity, Islam, Sikhism, as well as many other religions. (Full article...) Featured article Darjeeling (/dɑːrˈdʒiːlɪŋ/, Bengali: [ˈdarˌdʒiliŋ], Nepali: [ˈdard͡ziliŋ]) is a city in the northernmost region of the Indian state of West Bengal. Located in the Eastern Himalayas, it has an average elevation of 2,045 metres (6,709 ft). To the west of Darjeeling lies the easternmost province of Nepal, to the east the Kingdom of Bhutan, to the north the Indian state of Sikkim, and farther north the Tibet Autonomous Region region of China. Bangladesh lies to the south and southeast, and most of the state of West Bengal lies to the south and southwest, connected to the Darjeeling region by a narrow tract. Kangchenjunga, the world's third-highest mountain, rises to the north and is prominently visible on clear days. In the early 19th century, during East India Company rule in India, Darjeeling was identified as a potential summer retreat for British officials, soldiers and their families. The narrow mountain ridge was leased from the Kingdom of Sikkim, and eventually annexed to British India. Experimentation with growing tea on the slopes below Darjeeling was highly successful. Thousands of labourers were recruited chiefly from Nepal to clear the forests, build European-style cottages and work in the tea plantations. The widespread deforestation displaced the indigenous peoples. Residential schools were established in and around Darjeeling for the education of children of the domiciled British in India. By the late-19th century, a novel narrow-gauge mountain railway, the Darjeeling Himalayan Railway, was bringing summer residents into the town and carrying a freight of tea out for export to the world. After India's independence in 1947, as the British left Darjeeling, its cottages were purchased by wealthy Indians from the plains and its tea plantations by out-of-town Indian business owners and conglomerates. (Full article...)Selected Country Cyprus (/ˈsaɪprəs/ ), officially the Republic of Cyprus, is an island country in the eastern Mediterranean Sea, north of the Sinai Peninsula, south of the Anatolian Peninsula, and west of the Levant. It is geographically a part of West Asia, but its cultural ties and geopolitics are overwhelmingly Southeast European. Cyprus is the third-largest and third-most populous island in the Mediterranean. It is east of Greece, north of Egypt, south of Turkey, and west of Lebanon and Syria. Its capital and largest city is Nicosia. The northeast portion of the island is de facto governed by the self-declared Turkish Republic of Northern Cyprus. Cyprus is home to some of the oldest water wells in the world. Cyprus was settled by Mycenaean Greeks in two waves in the 2nd millennium BC. As a strategic location in the Eastern Mediterranean, it was subsequently occupied by several major powers, including the empires of the Assyrians, Egyptians and Persians, from whom the island was seized in 333 BC by Alexander the Great. Subsequent rule by Ptolemaic Egypt, the Classical and Eastern Roman Empire, Arab caliphates for a short period, the French Lusignan dynasty and the Venetians was followed by over three centuries of Ottoman rule between 1571 and 1878 (de jure until 1914). (Full article...)
Featured biographyAlexander II Theos Epiphanes Nikephoros (Ancient Greek: Ἀλέξανδρος Θεός Ἐπιφανής Νικηφόρος Áléxandros Theós Épiphanḗs Nikēphóros, surnamed Zabinas; c. 150 BC – 123 BC) was a Hellenistic Seleucid monarch who reigned as the King of Syria between 128 BC and 123 BC. His true parentage is debated; depending on which ancient historian, he either claimed to be a son of Alexander I or an adopted son of Antiochus VII. Most ancient historians and the modern academic consensus maintain that Alexander II's claim to be a Seleucid was false. His surname "Zabinas" (Ζαβίνας) is a Semitic name that is usually translated as "the bought one". It is possible, however, that Alexander II was a natural son of Alexander I, as the surname can also mean "bought from the god". The iconography of Alexander II's coinage indicates he based his claims to the throne on his descent from Antiochus IV, the father of Alexander I. Alexander II's rise is connected to the dynastic feuds of the Seleucid Empire. Both King Seleucus IV (d. 175 BC) and his brother Antiochus IV (d. 164 BC) had descendants contending for the throne, leading the country to experience many civil wars. The situation was complicated by Ptolemaic Egyptian interference, which was facilitated by the dynastic marriages between the two royal houses. In 128 BC, King Demetrius II of Syria, the representative of Seleucus IV's line, invaded Egypt to help his mother-in-law Cleopatra II who was engaged in a civil war against her brother and husband King Ptolemy VIII. Angered by the Syrian invasion, the Egyptian king instigated revolts in the cities of Syria against Demetrius II and chose Alexander II, a supposed representative of Antiochus IV's line, as an anti-king. With Egyptian troops, Alexander II captured the Syrian capital Antioch in 128 BC and warred against Demetrius II, defeating him decisively in 125 BC. The beaten king escaped to his wife Cleopatra Thea in the city of Ptolemais, but she expelled him. He was killed while trying to find refuge in the city of Tyre. (Full article...)General imagesThe following are images from various Asia-related articles on Wikipedia. Featured picture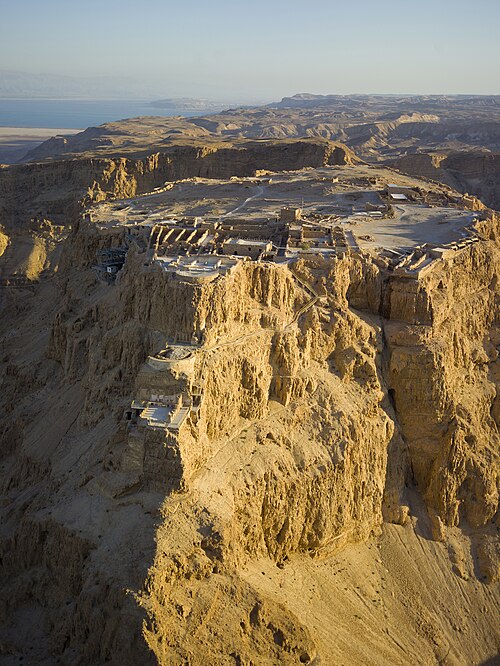 Credit: Photograph: Andrew Shiva An aerial view of Masada, an ancient fortification in the Southern District of Israel. Found atop an isolated rock plateau, it overlooks the Dead Sea. The first fortifications on the mountain were built by Alexander Jannaeus, and significantly strengthened by the Roman client king Herod between 37 and 31 BCE. During the First Jewish–Roman War of 66–73 CE, the fortress was besieged, falling only after the 960 Sicarii defending it committed mass suicide.
Masada is among the more popular tourist attractions in Israel, and in 2001 it was made a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
Did you know...
Updated: 6:33, 14 February 2024 In the news
Related portalsMajor Religions in Asia Middle East Central Asia and Surroundings Indian Subcontinent Southeast Asia East Asia Selected panorama
The Central Area of Singapore surrounded by the perimeter of five planning areas: the Marina Bay, the Downtown Core, Marina East, Marina South and Straits View. The area surrounding the bay itself, also called Marina Bay, is a 360 hectare extension to the adjacent CBD. It is also the new downtown of Singapore built on reclaimed land. TopicsCategoriesAssociated WikimediaThe following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
More portalsShortcuts to this page: Asia portal • P:ASIA Purge server cache |
© MMXXIII Rich X Search. We shall prevail. All rights reserved. Rich X Search




























































































